Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3667 |
3611 |
24.33 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3526 |
3472 |
18.51 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3047 |
3001 |
55.74 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3044 |
2997 |
42.91 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3022 |
2976 |
3.75 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3006 |
2960 |
17.79 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2981 |
2935 |
41.23 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2970 |
2925 |
28.72 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2968 |
2922 |
12.37 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1706 |
1680 |
311.04 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1585 |
1561 |
86.78 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1480 |
1457 |
6.60 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1472 |
1450 |
6.80 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1465 |
1442 |
1.58 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1441 |
1419 |
7.35 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1385 |
1364 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1364 |
1344 |
57.19 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1333 |
1313 |
28.65 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1295 |
1275 |
32.08 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1248 |
1229 |
50.73 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1226 |
1208 |
22.91 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1111 |
1094 |
1.77 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1092 |
1076 |
3.46 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1036 |
1020 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1024 |
1008 |
5.09 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
904 |
890 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
869 |
856 |
1.19 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
835 |
822 |
2.49 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
737 |
726 |
3.11 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
680 |
670 |
2.81 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
595 |
586 |
10.05 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
522 |
514 |
7.08 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
420 |
413 |
2.63 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
333 |
328 |
1.14 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
243 |
240 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
187 |
184 |
6.34 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
167 |
165 |
164.88 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
84 |
82 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
10i |
10i |
5.43 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28029.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9847) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27601.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
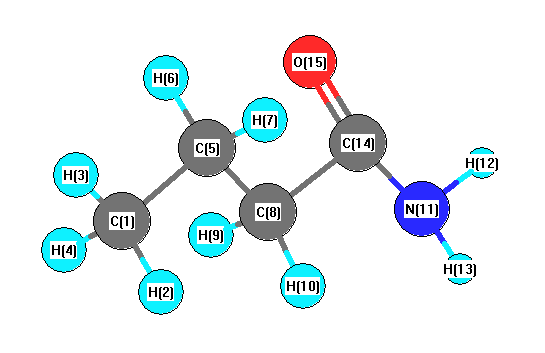
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.574 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.149 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.105 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.096 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.053 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.142 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.042 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.008 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.654 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.801 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.098 |
-3.545 |
-0.197 |
3.552 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-34.448 |
-6.609 |
-0.994 |
| y |
-6.609 |
-39.536 |
0.057 |
| z |
-0.994 |
0.057 |
-38.308 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.474 |
-6.609 |
-0.994 |
| y |
-6.609 |
-3.158 |
0.057 |
| z |
-0.994 |
0.057 |
-1.316 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.632 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.088 |
|---|
| xy | -6.609 |
|---|
| xz | -0.994 |
|---|
| yz | 0.057 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
11.895 |
-0.356 |
-0.333 |
| y |
-0.356 |
9.928 |
0.029 |
| z |
-0.333 |
0.029 |
8.052 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
217.774 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.757 |