Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/3-21G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -150.275415 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -150.283289 |
| HF Energy | -150.275415 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/3-21G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3296 |
3240 |
19.32 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
3024 |
2972 |
41.53 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1701 |
1672 |
25.58 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
1496 |
1471 |
2.15 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
1046 |
1029 |
39.08 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A1 |
718 |
706 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A1 |
433 |
426 |
6.22 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A2 |
3401 |
3343 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A2 |
1399 |
1375 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A2 |
1080 |
1062 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A2 |
283 |
278 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B1 |
3402 |
3344 |
11.28 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B1 |
3075 |
3022 |
28.49 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B1 |
1355 |
1332 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B1 |
822 |
808 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B1 |
442 |
435 |
115.52 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B2 |
3294 |
3238 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B2 |
1686 |
1658 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B2 |
1378 |
1354 |
4.38 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B2 |
998 |
981 |
13.14 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B2 |
598 |
588 |
576.21 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17463.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.983) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17166.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/3-21G
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.557 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.292 |
-0.186 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
-1.292 |
-0.186 |
| H4 |
0.889 |
0.000 |
1.201 |
| H5 |
-0.889 |
0.000 |
1.201 |
| H6 |
0.837 |
1.374 |
-0.783 |
| H7 |
-0.837 |
1.374 |
-0.783 |
| H8 |
-0.837 |
-1.374 |
-0.783 |
| H9 |
0.837 |
-1.374 |
-0.783 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.4900 | 1.4900 | 1.0980 | 1.0980 | 2.0938 | 2.0938 | 2.0938 | 2.0938 |
N2 | 1.4900 | | 2.5832 | 2.0935 | 2.0935 | 1.0315 | 1.0315 | 2.8569 | 2.8569 | N3 | 1.4900 | 2.5832 | | 2.0935 | 2.0935 | 2.8569 | 2.8569 | 1.0315 | 1.0315 | H4 | 1.0980 | 2.0935 | 2.0935 | | 1.7786 | 2.4138 | 2.9672 | 2.9672 | 2.4138 | H5 | 1.0980 | 2.0935 | 2.0935 | 1.7786 | | 2.9672 | 2.4138 | 2.4138 | 2.9672 | H6 | 2.0938 | 1.0315 | 2.8569 | 2.4138 | 2.9672 | | 1.6745 | 3.2178 | 2.7478 | H7 | 2.0938 | 1.0315 | 2.8569 | 2.9672 | 2.4138 | 1.6745 | | 2.7478 | 3.2178 | H8 | 2.0938 | 2.8569 | 1.0315 | 2.9672 | 2.4138 | 3.2178 | 2.7478 | | 1.6745 | H9 | 2.0938 | 2.8569 | 1.0315 | 2.4138 | 2.9672 | 2.7478 | 3.2178 | 1.6745 | |
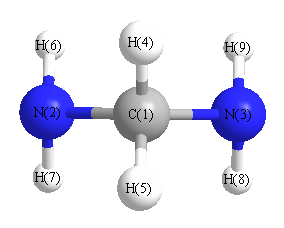 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
H6 |
111.880 |
|
C1 |
N2 |
H7 |
111.880 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H8 |
111.880 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H9 |
111.880 |
| N2 |
C1 |
N3 |
121.396 |
|
N2 |
C1 |
H4 |
106.610 |
| N2 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.610 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
106.610 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.610 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.525 |
| H6 |
N2 |
H7 |
109.104 |
|
H8 |
N3 |
H9 |
109.104 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/3-21G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.163 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.648 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.648 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.222 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.222 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.254 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.254 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.254 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.254 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.203 |
2.203 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-16.492 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-25.624 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.569 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.105 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-8.594 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.488 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.977 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.133 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.733 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.746 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.215 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
55.399 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.443 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/3-21G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -150.269449 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -150.277283 |
| HF Energy | -150.269449 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/3-21G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3450 |
3392 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3332 |
3276 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2842 |
2794 |
140.65 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1668 |
1639 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1564 |
1538 |
4.46 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1358 |
1335 |
3.04 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1176 |
1156 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
934 |
918 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
724 |
712 |
241.04 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
470 |
462 |
4.96 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
309 |
304 |
15.72 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B |
3450 |
3392 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B |
3332 |
3275 |
13.05 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B |
2849 |
2800 |
156.93 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
1659 |
1631 |
50.51 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
1435 |
1411 |
34.53 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
1232 |
1211 |
19.59 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
1105 |
1086 |
21.53 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
960 |
944 |
3.97 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
657 |
646 |
200.43 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
278 |
273 |
112.23 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17392.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.983) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17097.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/3-21G
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.568 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.181 |
-0.319 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
-1.181 |
-0.319 |
| H4 |
0.887 |
-0.112 |
1.230 |
| H5 |
-0.887 |
0.112 |
1.230 |
| H6 |
-0.086 |
2.061 |
0.204 |
| H7 |
0.847 |
1.182 |
-0.903 |
| H8 |
0.086 |
-2.061 |
0.204 |
| H9 |
-0.847 |
-1.182 |
-0.903 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.4775 | 1.4775 | 1.1129 | 1.1129 | 2.0949 | 2.0684 | 2.0949 | 2.0684 |
N2 | 1.4775 | | 2.3624 | 2.2052 | 2.0813 | 1.0278 | 1.0284 | 3.2857 | 2.5772 | N3 | 1.4775 | 2.3624 | | 2.0813 | 2.2052 | 3.2857 | 2.5772 | 1.0278 | 1.0284 | H4 | 1.1129 | 2.2052 | 2.0813 | | 1.7887 | 2.5931 | 2.4957 | 2.3438 | 2.9500 | H5 | 1.1129 | 2.0813 | 2.2052 | 1.7887 | | 2.3438 | 2.9500 | 2.5931 | 2.4957 | H6 | 2.0949 | 1.0278 | 3.2857 | 2.5931 | 2.3438 | | 1.6940 | 4.1262 | 3.5106 | H7 | 2.0684 | 1.0284 | 2.5772 | 2.4957 | 2.9500 | 1.6940 | | 3.5106 | 2.9079 | H8 | 2.0949 | 3.2857 | 1.0278 | 2.3438 | 2.5931 | 4.1262 | 3.5106 | | 1.6940 | H9 | 2.0684 | 2.5772 | 1.0284 | 2.9500 | 2.4957 | 3.5106 | 2.9079 | 1.6940 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
H6 |
112.957 |
|
C1 |
N2 |
H7 |
110.590 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H8 |
112.957 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H9 |
110.590 |
| N2 |
C1 |
N3 |
106.967 |
|
N2 |
C1 |
H4 |
115.619 |
| N2 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.237 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
106.237 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H5 |
115.619 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.508 |
| H6 |
N2 |
H7 |
110.591 |
|
H8 |
N3 |
H9 |
110.591 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/3-21G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.087 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.657 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.657 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.260 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.260 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.406 |
1.406 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.566 |
2.979 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.979 |
-15.595 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.987 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.776 |
2.979 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.979 |
4.181 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.406 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.812 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.971 |
|---|
| xy | 2.979 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.948 |
-0.118 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.118 |
4.550 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.557 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
53.463 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.312 |
