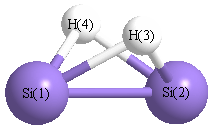Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.990919 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.990919 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.659772 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2294 |
2294 |
0.00 |
279.88 |
0.33 |
0.49 |
| 2 |
Σg |
735 |
735 |
0.00 |
83.97 |
0.21 |
0.35 |
| 3 |
Σu |
2291 |
2291 |
0.01 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
Πg |
618i |
618i |
0.00 |
69.29 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
Πg |
618i |
618i |
0.00 |
69.29 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
Πu |
401 |
401 |
3.70 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Πu |
401 |
401 |
3.70 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2443.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2443.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.994 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.994 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.464 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.464 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9875 | 1.4699 | 3.4574 |
Si2 | 1.9875 | | 3.4574 | 1.4699 | H3 | 1.4699 | 3.4574 | | 4.9273 | H4 | 3.4574 | 1.4699 | 4.9273 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.022 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.022 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.022 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.022 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.779 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-29.779 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-20.101 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.839 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.839 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.677 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 19.355 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.034 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.034 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
14.466 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.374 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.508 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.026605 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.026605 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.427987 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2113 |
2113 |
0.00 |
378.19 |
0.46 |
0.63 |
| 2 |
Ag |
615 |
615 |
0.00 |
41.14 |
0.58 |
0.73 |
| 3 |
Ag |
555 |
555 |
0.00 |
60.64 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 4 |
Au |
236 |
236 |
63.51 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Bu |
2119 |
2119 |
165.55 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
Bu |
234 |
234 |
39.46 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2935.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2935.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
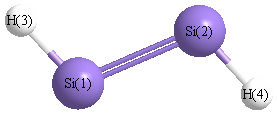
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.061 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.061 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.244 |
1.907 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.244 |
-1.907 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1228 | 1.5043 | 3.2189 |
Si2 | 2.1228 | | 3.2189 | 1.5043 | H3 | 1.5043 | 3.2189 | | 4.5543 | H4 | 3.2189 | 1.5043 | 4.5543 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
124.222 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
124.222 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.035 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.035 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.035 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.035 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.243 |
0.156 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.156 |
-23.177 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.528 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.391 |
0.156 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.156 |
6.209 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.818 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -9.636 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.066 |
|---|
| xy | 0.156 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.003 |
-0.023 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.023 |
15.146 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.607 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
58.976 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.680 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.051928 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.051928 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.086930 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1581 |
1581 |
9.47 |
53.99 |
0.07 |
0.14 |
| 2 |
A1 |
934 |
934 |
41.21 |
2.48 |
0.52 |
0.69 |
| 3 |
A1 |
510 |
510 |
1.04 |
59.98 |
0.36 |
0.53 |
| 4 |
A2 |
1051 |
1051 |
0.00 |
3.78 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B1 |
1522 |
1522 |
31.46 |
20.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
1114 |
1114 |
322.40 |
2.52 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3355.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3355.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.119 |
-0.053 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.119 |
-0.053 |
| H3 |
0.996 |
0.000 |
0.741 |
| H4 |
-0.996 |
0.000 |
0.741 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2379 | 1.6957 | 1.6957 |
Si2 | 2.2379 | | 1.6957 | 1.6957 | H3 | 1.6957 | 1.6957 | | 1.9929 | H4 | 1.6957 | 1.6957 | 1.9929 | |
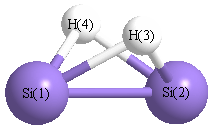 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.709 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.709 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.109 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.109 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.287 |
0.287 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.811 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-31.754 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.624 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.378 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.537 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.158 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.317 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.943 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.090 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.571 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.207 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.165 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.494 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -580.037888 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.037888 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.518095 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2113 |
2113 |
106.00 |
271.99 |
0.40 |
0.57 |
| 2 |
A' |
1608 |
1608 |
89.31 |
76.23 |
0.25 |
0.40 |
| 3 |
A' |
999 |
999 |
117.24 |
5.04 |
0.46 |
0.63 |
| 4 |
A' |
597 |
597 |
14.84 |
53.87 |
0.32 |
0.48 |
| 5 |
A' |
452 |
452 |
5.34 |
3.39 |
0.06 |
0.11 |
| 6 |
A" |
144 |
144 |
41.85 |
10.04 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2956.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2956.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.061 |
-1.152 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.061 |
0.982 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.264 |
-0.009 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.457 |
2.392 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1342 | 1.7501 | 3.5817 |
Si2 | 2.1342 | | 1.6545 | 1.5021 | H3 | 1.7501 | 1.6545 | | 2.5325 | H4 | 3.5817 | 1.5021 | 2.5325 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
159.810 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.209 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.108 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.008 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.088 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.126 |
0.827 |
0.000 |
0.837 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.586 |
0.161 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.161 |
-25.622 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.792 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.621 |
0.161 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.161 |
3.067 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.688 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -9.376 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.964 |
|---|
| xy | 0.161 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.711 |
0.019 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.019 |
14.402 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.427 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
57.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.550 |