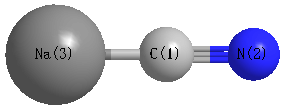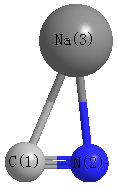Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.088871 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.088214 |
| HF Energy | -255.088871 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 46.178135 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.701 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.871 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.573 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1702 | 2.2744 |
N2 | 1.1702 | | 3.4446 | Na3 | 2.2744 | 3.4446 | |
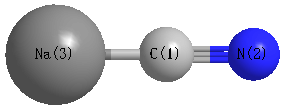 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.305 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.153 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.458 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.555 |
10.555 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.323 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.323 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-13.295 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.014 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-2.014 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.029 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.058 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.387 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.387 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.713 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
64.670 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.042 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.092796 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.092523 |
| HF Energy | -255.092796 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 51.136741 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.092 |
0.667 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.118 |
0.000 |
| Na3 |
-0.596 |
-1.076 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1813 | 2.4261 |
N2 | 1.1813 | | 2.2730 | Na3 | 2.4261 | 2.2730 | |
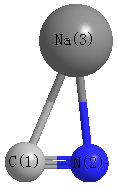 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
86.113 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
28.744 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
65.143 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.178 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.365 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.597 |
-7.415 |
0.000 |
8.724 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.801 |
3.526 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.526 |
-13.941 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.449 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.106 |
3.526 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.526 |
4.685 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.578 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.157 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.861 |
|---|
| xy | 3.526 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.764 |
0.099 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.099 |
4.396 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
-0.000 |
3.510 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.861 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.772 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.089336 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.088434 |
| HF Energy | -255.089336 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 48.313861 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.869 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.689 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.458 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1804 | 3.3265 |
N2 | 1.1804 | | 2.1461 | Na3 | 3.3265 | 2.1461 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.359 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.594 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.787 |
10.787 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.341 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.341 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-15.936 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.703 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.703 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.405 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.810 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.380 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
3.381 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.246 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
58.185 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.628 |