Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3667 |
3616 |
21.56 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3527 |
3478 |
16.97 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3048 |
3006 |
56.50 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3044 |
3002 |
45.78 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3022 |
2979 |
6.58 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3000 |
2958 |
21.82 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2984 |
2942 |
35.06 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2970 |
2929 |
32.21 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2963 |
2921 |
13.91 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1722 |
1698 |
272.40 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1583 |
1561 |
89.67 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1481 |
1461 |
5.84 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1474 |
1453 |
6.35 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1466 |
1446 |
1.62 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1435 |
1414 |
6.52 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1388 |
1369 |
0.93 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1368 |
1349 |
55.32 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1332 |
1314 |
26.28 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1294 |
1276 |
34.90 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1244 |
1227 |
50.29 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1227 |
1210 |
16.13 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1111 |
1095 |
1.19 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1094 |
1078 |
2.18 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1043 |
1028 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1026 |
1012 |
4.08 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
907 |
894 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
869 |
857 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
827 |
815 |
3.59 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
736 |
726 |
3.90 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
664 |
655 |
3.07 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
601 |
593 |
11.98 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
513 |
506 |
5.23 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
417 |
411 |
2.10 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
336 |
331 |
1.75 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
241 |
238 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
184 |
181 |
6.83 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
162 |
160 |
164.98 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
86 |
85 |
1.69 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
31i |
31i |
5.31 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28012.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.986) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27619.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
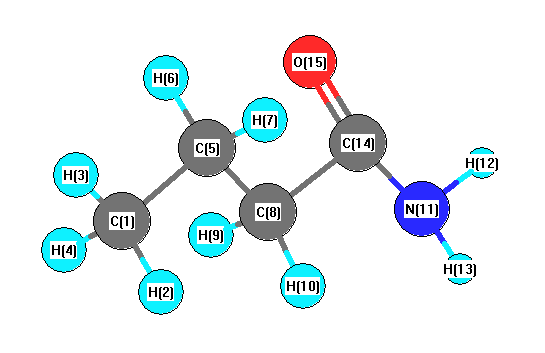
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.267 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.078 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.106 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.071 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.150 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.061 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.193 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.192 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.324 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.215 |
-3.477 |
-0.093 |
3.485 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.433 |
-6.379 |
-0.536 |
| y |
-6.379 |
-39.061 |
-0.134 |
| z |
-0.536 |
-0.134 |
-37.988 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.092 |
-6.379 |
-0.536 |
| y |
-6.379 |
-3.350 |
-0.134 |
| z |
-0.536 |
-0.134 |
-1.741 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.483 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.628 |
|---|
| xy | -6.379 |
|---|
| xz | -0.536 |
|---|
| yz | -0.134 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
11.058 |
-0.384 |
-0.258 |
| y |
-0.384 |
9.114 |
0.038 |
| z |
-0.258 |
0.038 |
7.087 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
218.128 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.769 |