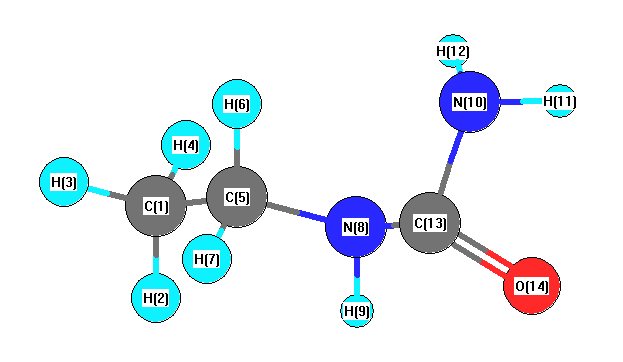
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3629 |
3578 |
24.74 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3566 |
3516 |
21.22 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3509 |
3460 |
8.37 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3066 |
3023 |
27.18 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3051 |
3009 |
35.56 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2985 |
2943 |
24.62 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2957 |
2916 |
34.99 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2936 |
2895 |
48.14 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1736 |
1712 |
449.30 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1596 |
1573 |
122.87 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1501 |
1480 |
2.84 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1477 |
1456 |
4.79 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1468 |
1447 |
6.15 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1428 |
1408 |
6.96 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1389 |
1370 |
62.17 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1383 |
1364 |
197.98 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1338 |
1319 |
40.32 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1278 |
1260 |
3.01 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1167 |
1150 |
14.55 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1142 |
1126 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1101 |
1085 |
42.58 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1039 |
1024 |
15.31 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
965 |
952 |
1.78 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
875 |
863 |
1.85 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
811 |
800 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
747 |
736 |
33.35 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
580 |
572 |
49.63 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
544 |
536 |
17.78 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
521 |
514 |
112.19 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
476 |
469 |
28.82 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
377 |
372 |
93.22 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
356 |
351 |
1.40 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
263 |
260 |
2.32 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
193 |
191 |
3.12 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
101 |
99 |
5.62 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
37 |
37 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25792.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.986) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25431.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.272 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.030 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.057 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
N |
-0.127 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.133 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.230 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.138 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.353 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-3.148 |
2.617 |
-0.576 |
4.134 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.679 |
6.798 |
-1.514 |
| y |
6.798 |
-35.256 |
-1.720 |
| z |
-1.514 |
-1.720 |
-37.971 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.066 |
6.798 |
-1.514 |
| y |
6.798 |
3.069 |
-1.720 |
| z |
-1.514 |
-1.720 |
-1.003 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.007 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.423 |
|---|
| xy | 6.798 |
|---|
| xz | -1.514 |
|---|
| yz | -1.720 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.731 |
-0.063 |
0.078 |
| y |
-0.063 |
8.687 |
-0.059 |
| z |
0.078 |
-0.059 |
6.176 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
203.791 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.276 |