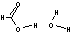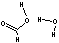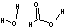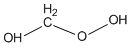Methods with standard basis sets
|
|
STO-3G |
3-21G |
3-21G* |
6-31G |
6-31G* |
6-31G** |
6-31+G** |
6-311G* |
6-311G** |
6-31G(2df,p) |
6-311+G(3df,2p) |
6-311+G(3df,2pd) |
TZVP |
cc-pVDZ |
cc-pVTZ |
aug-cc-pVDZ |
aug-cc-pVTZ |
cc-pV(T+d)Z |
daug-cc-pVTZ |
| hartree fock |
HF |
|
0.0 a
45.5 b
43.0 c |
|
|
0.0 a
25.1 b
18.9 c
364.7 d |
|
0.0 a
20.1 b
14.5 c |
|
|
|
0.0 a
17.4 b
11.5 c |
0.0 a
17.5 b
11.6 c |
0.0 a
25.1 b
18.9 c
65.6 d |
|
|
|
0.0 a
17.0 b
11.5 c |
|
0.0 a
16.9 b
11.4 c
378.8 d |
| density functional |
BLYP |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
40.1 b
33.3 c
333.7 d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B1B95 |
0.0 a
-9457.5 b
-9463.8 c |
0.0 a
-3823.7 b
67.3 c |
0.0 a
67.3 c |
0.0 a
-190.3 b
-196.6 c |
0.0 a
22.6 b
30.0 c |
0.0 a
81.8 b
75.4 c |
0.0 a
25.5 b
20.6 c |
0.0 a
29.7 c |
0.0 a
82.4 c |
0.0 a
130.3 b
124.0 c |
|
|
|
0.0 a
127.4 b
121.0 c |
0.0 a
363.1 b
356.7 c |
0.0 a
211.2 b
204.9 c |
|
0.0 a
363.1 b
356.7 c |
|
| B3LYP |
|
0.0 a
70.2 b
69.2 c |
|
|
0.0 a
38.2 b
30.9 c |
|
0.0 a
26.1 b
19.9 c |
|
|
0.0 a
35.8 b
28.8 c
350.9 d |
|
0.0 a
23.8 b
17.1 c |
0.0 a
27.3 b
21.4 c
358.9 d |
|
|
|
0.0 a
23.4 b
17.0 c
355.5 d |
|
|
| B3LYPultrafine |
|
0.0 a
70.2 b
69.2 c |
|
|
0.0 a
38.1 b
30.9 c |
|
0.0 a
26.0 b
19.9 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
23.8 b
17.1 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
23.2 b
16.7 c |
|
|
| M06-2X |
|
|
0.0 a
69.5 b
69.0 c
316.1 d |
|
0.0 a
37.1 b
29.6 c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PBEPBE |
|
0.0 a
87.0 b
86.1 c |
|
|
0.0 a
45.0 b
37.6 c |
|
0.0 a
30.3 b
23.9 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
28.5 b
21.4 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
27.9 b
21.2 c |
|
|
| PBEPBEultrafine |
|
0.0 a
87.0 b
86.2 c |
|
|
0.0 a
45.0 b
37.6 c |
|
0.0 a
30.2 b
23.7 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
28.5 b
21.4 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
27.9 b
21.0 c |
|
|
| PBE1PBE |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
32.5 c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| HSEh1PBE |
|
0.0 a
40.9 b
33.1 c |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
40.9 b
33.1 c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
40.9 b
33.1 c |
|
|
|
|
| TPSSh |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
40.2 b
33.0 c
322.5 d |
|
0.0 a
22.1 c
333.3 d |
|
|
0.0 a
37.9 b
30.9 c
333.2 d |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
30.6 b
24.8 c
337.0 d |
|
|
|
|
| wB97X-D |
|
|
0.0 a
66.1 b
64.6 c
302.5 d |
|
0.0 a
37.0 b
31.4 c
342.8 d |
|
0.0 a
27.5 b
356.3 d |
|
0.0 a
33.0 b
27.9 c
367.1 d |
|
|
|
0.0 a
28.8 b
361.6 d |
0.0 a
27.5 b
356.3 d |
0.0 a
29.3 b
23.1 c
359.7 d |
|
0.0 a
26.0 b
19.0 c
358.2 d |
|
|
| B97D3 |
|
0.0 a
74.1 b
73.5 c
313.5 d |
|
|
0.0 a
39.1 b
32.4 c
344.6 d |
|
0.0 a
26.8 b
20.4 c
354.9 d |
|
0.0 a
33.0 b
27.6 c
367.3 d |
|
0.0 a
24.6 b
17.9 c
361.3 d |
|
0.0 a
28.1 b
22.4 c
361.8 d |
|
0.0 a
29.1 b
23.6 c
360.1 d |
|
0.0 a
24.2 b
17.9 c
357.4 d |
|
|
| |
STO-3G |
3-21G |
3-21G* |
6-31G |
6-31G* |
6-31G** |
6-31+G** |
6-311G* |
6-311G** |
6-31G(2df,p) |
6-311+G(3df,2p) |
6-311+G(3df,2pd) |
TZVP |
cc-pVDZ |
cc-pVTZ |
aug-cc-pVDZ |
aug-cc-pVTZ |
cc-pV(T+d)Z |
daug-cc-pVTZ |
|---|
| Moller Plesset perturbation |
MP2 |
|
0.0 a
52.2 b
53.2 c |
|
|
0.0 a
32.9 b
27.1 c
368.0 d |
|
0.0 a
23.4 b
18.6 c |
0.0 a
31.4 b
26.6 c
377.2 d |
|
|
|
0.0 a
23.1 b
17.3 c |
0.0 a
23.6 b
19.4 c
377.6 d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| MP3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
28.7 b
23.0 c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| MP3=FULL |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
30.0 b
24.1 c
347.3 d |
|
0.0 a
22.2 b
17.0 c
354.6 d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B2PLYP |
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
36.2 b
29.4 c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 a
28.2 b
22.4 c
365.3 d |
|
|
|
|
| Coupled Cluster |
CCSD(T) |
|
0.0 a
50.1 c |
|
|
0.0 a
1891.3 b
24.9 c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
STO-3G |
3-21G |
3-21G* |
6-31G |
6-31G* |
6-31G** |
6-31+G** |
6-311G* |
6-311G** |
6-31G(2df,p) |
6-311+G(3df,2p) |
6-311+G(3df,2pd) |
TZVP |
cc-pVDZ |
cc-pVTZ |
aug-cc-pVDZ |
aug-cc-pVTZ |
cc-pV(T+d)Z |
daug-cc-pVTZ |
|---|