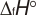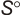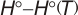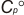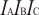Geometric Data

Point Group Cs
Internal coordinates
distances (r) in Å, angles (a) in degrees, dihedrals (d) in degrees
Cartesians
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
| C1 |
0.0000 |
0.0000 |
0.0000 |
| H2 |
1.0800 |
0.0000 |
0.0000 |
| O3 |
-0.5899 |
1.0427 |
0.0000 |
Atom - Atom Distances 
Distances in Å
| |
C1 |
H2 |
O3 |
| C1 |
|
1.0800 | 1.1980 |
| H2 |
1.0800 |
|
1.9687 |
| O3 |
1.1980 | 1.9687 |
|
Calculated geometries
for HCO
- (formyl anion).
Experimental Bond Angles (degrees) from cartesians 
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| H2 |
C1 |
O3 |
119.500 |
Bond descriptions
Examples: C-C single bond, C=C, double bond, C#C triple bond, C:C aromatic bond
| Bond Type |
Count |
| H-C |
1 |
| C=O |
1 |
Connectivity
| Atom 1 |
Atom 2 |
| C1 |
H2 |
| C1 |
O3 |